- Home
- About Us
- Products
- Wires & Cables
- Automotive wires & cables
- Braid tubular
- Composite PI/PTFE Insulated Wire and Cable
- Control/ signal/ instrumentation/ communication cable
- Fire survival cable
- Fluoropolymer Wires (PTFE/FEP/ETFE/PFA)
- LSZH/ FRLSZH/ ZHFR Cable
- Multi-core Shielded/ Unshielded Composite Cables
- PVC Wire Cable
- RG Cables
- RTD Cable
- Rubber Cable
- Silicone Cable
- Spiral Cable/ Curly Cord
- Submersible winding wires & 3 core flat cables
- Thermocouple and Extension Grade Cables
- TPU Cable
- UL Cable
- XLPE Insulated Wire & Cable
- Under floor Heating and Accessories
- Wiring Harness
- PV Ribbon
- Flexible printed Electroincs
- Power Cord
- Wires & Cables
- Certificates
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Contact Us
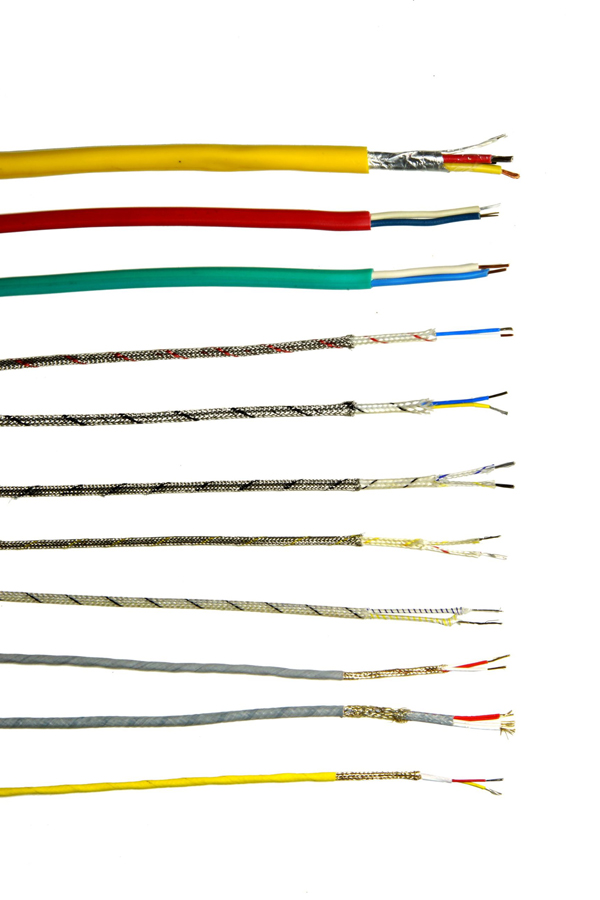

A thermocouple is a device used to measure temperature based on the principle of the Seebeck effect, which generates a voltage proportional to the temperature difference between two dissimilar electrical conductors, or metals, that form an electrical junction.
The voltage/ emf produced by the junction can be interpreted to measure temperature, making thermocouples a widely used temperature sensor in various applications.
There are several types of thermocouples, each with its unique characteristics and applications. The most common types include B, E, J, K, N, R, S, T, and C, with different base metals such as iron, copper, nickel, platinum, rhodium, and Chromel. Each type has its temperature range, resistance, and durability, making them suitable for different applications.
| STANDARDS | |
| Type | Din 43713, IEC 60584-3, ABSU/MC96.1, JIS C 1610, IS 8784 |
| TECHNICAL DATA | |
| Operating Voltage | Upto 1100 Volts AC |
| High Voltage Testing | 2 kV AC for 1 second core to core |
| Max. Temperature | Upto 70 deg. C for PVC, 90 deg. C for HRPVC and upto 250 deg. C for PTFE/ PFA |
| Bending radius | 7.5 x cable dia. |
| CONSTRUCTION | |
| Conductor | Refer attached PDF file |
| Insulation | PE/ XLPE/ PVC/ HRPV/ PTFE/ FEP/ PFA |
| Shield Options | SS/TPC/NPC & Al. Mylar with drain wire |
| Jacket | PTFE/ FEP/ PFA/ PVC/ ZHFR |